Introduction
Wildfires have become a serious concern in Manitoba, especially as seasons shift and climate patterns change. The growing frequency and intensity of these fires not only pose a threat to natural landscapes but also significantly impact communities, wildlife, and air quality. Understanding the current situation surrounding wildfires in Manitoba is crucial for residents, policy-makers, and environmentalists alike.
Current Situation
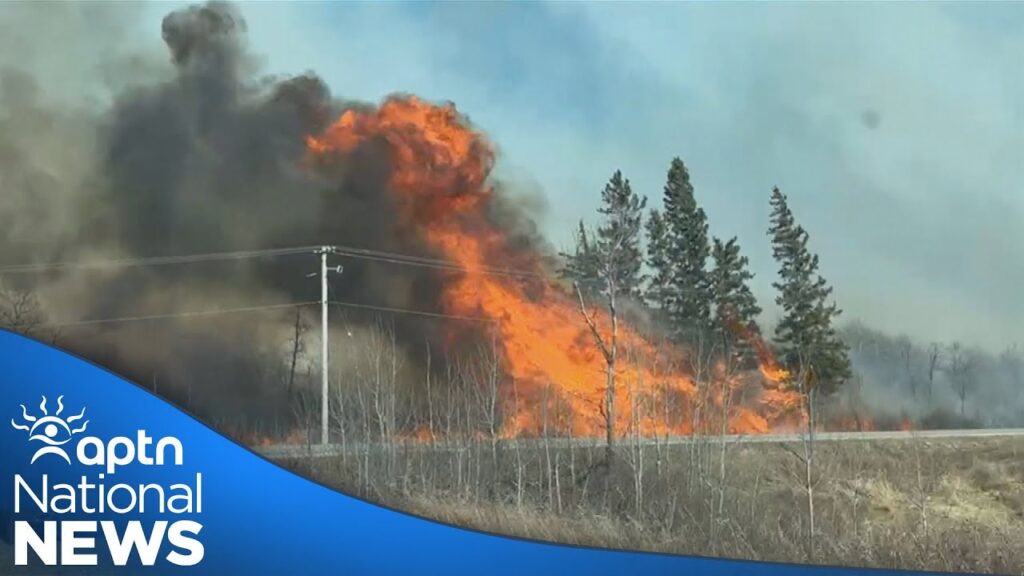
As of early August 2023, Manitoba has reported an alarming increase in wildfires compared to previous years. According to the Manitoba Wildfire Program, over 250 wildfires have been recorded since the start of the season, with over 100 fires currently active. The majority of these fires are concentrated in the eastern and northern regions of the province, where dry conditions and high winds have contributed to rapid fire spread.
The Manitoba government has issued multiple evacuation orders for communities at risk. For instance, in mid-July, residents of the community of Little Saskatchewan were forced to evacuate as nearby wildfires grew uncontrollably. Emergency responders have been working tirelessly to contain the fires, aided by additional resources from neighboring provinces and territories.
Causes and Contributing Factors
The causes of wildfires in Manitoba are multifaceted. Natural events such as lightning strikes trigger many wildfires, but human activity has also played a significant role. Inconsistent weather patterns, including prolonged droughts and extreme heatwaves during the summer months, have further increased the likelihood of wildfires spreading rapidly.
Moreover, the changing climate poses ongoing risks that can exacerbate fire conditions in the future. According to the Climate Change Action Plan released by the Manitoba Government, the province expects to see an increase in the frequency and intensity of wildfires due to rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns.
Impact on Communities and Environment
The impact of these wildfires is profound. Communities near fire-prone areas are facing challenges such as evacuations and loss of property. Additionally, the air quality has been noticeably affected, with smoke blanketing large areas of the province, prompting health warnings from authorities.
Conclusion
The ongoing wildfires in Manitoba underscore the urgent need for comprehensive fire management strategies and climate adaptation policies. As the province grapples with this crisis, it is essential for residents to stay informed about safety measures and evacuation protocols. With climate change expected to pose even greater challenges in the future, proactive approaches to wildfire prevention and response will be critical. Local communities, policymakers, and environmental organizations must collaborate to ensure that the region can effectively mitigate the devastating effects of wildfires.