Introduction
The topic of nuclear weapons remains critically important in global politics and security discussions. With nuclear arsenals capable of unprecedented destruction, the countries that possess these weapons play a significant role in shaping international relations and defense strategies. As of now, nine countries are recognized as nuclear-armed states, influencing global stability and non-proliferation efforts.
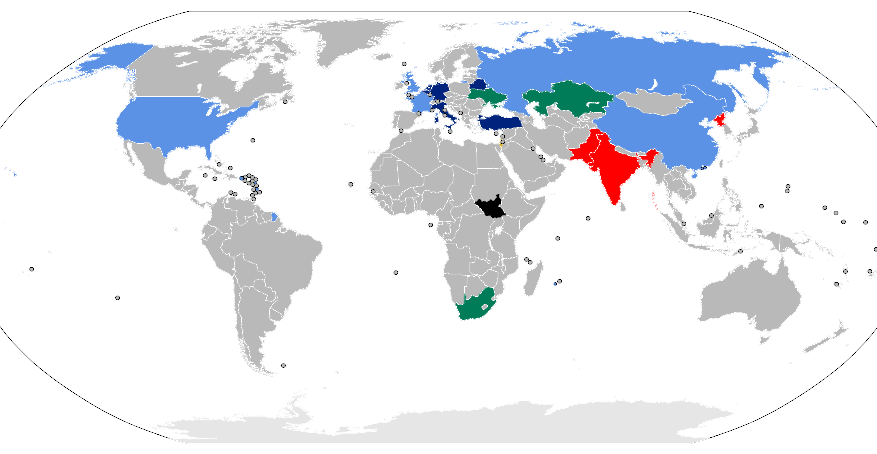
List of Countries with Nuclear Weapons
According to the latest reports by various defense organizations and governments, the countries that possess nuclear weapons include:
- United States: The first nation to develop nuclear weapons, the U.S. currently has approximately 5,800 nuclear warheads.
- Russia: Following the U.S., Russia maintains the largest nuclear arsenal, estimated at roughly 6,375 warheads.
- United Kingdom: The UK operates its nuclear forces under a policy of minimum credible deterrent, with around 225 warheads.
- France: France possesses about 290 nuclear warheads and maintains a nuclear strategy that includes both an airborne and submarine component.
- China: China has been modernizing its nuclear arsenal, currently estimated at around 320 warheads.
- India: India is believed to have approximately 160 nuclear warheads and follows a no-first-use policy.
- Pakistan: Pakistan is estimated to have around 170 nuclear warheads, with developments focused on both delivery and range capabilities.
- North Korea: North Korea’s nuclear program is shrouded in secrecy, but estimates suggest it possesses between 40 to 50 warheads.
- Israel: While Israel has not officially confirmed its nuclear arsenal, it is widely believed to have around 90 nuclear warheads.
Global Significance and Challenges
The existence of nuclear weapons poses various challenges to international security, including the threat of proliferation, regional tensions, and the potential for nuclear terrorism. Treaties such as the Treaty on the Non-Proliferation of Nuclear Weapons (NPT) aim to curb the spread of nuclear weapons and promote peaceful nuclear energy. However, challenges remain, particularly with countries like North Korea and ongoing conflicts that raise concerns over the use of these weapons.
Conclusion
The nuclear capabilities of these nine nations continue to shape global dynamics. Efforts towards disarmament and non-proliferation are vital to reducing the risk of nuclear conflict and promoting global security. As geopolitical tensions escalate in various regions, understanding the implications of nuclear arsenals remains crucial for individuals and policymakers alike. From diplomatic engagements to grassroots movements advocating for nuclear disarmament, the path forward requires collective action and commitment to peace.



