Introduction
The fluctuations in bank interest rates in Canada play a crucial role in shaping the country’s economic landscape. Changes to these rates significantly impact borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, influencing spending, saving, and investment decisions. This article explores the current state of bank interest rates in Canada, focusing on the implications for individuals and the broader economy.
Current Bank Interest Rates
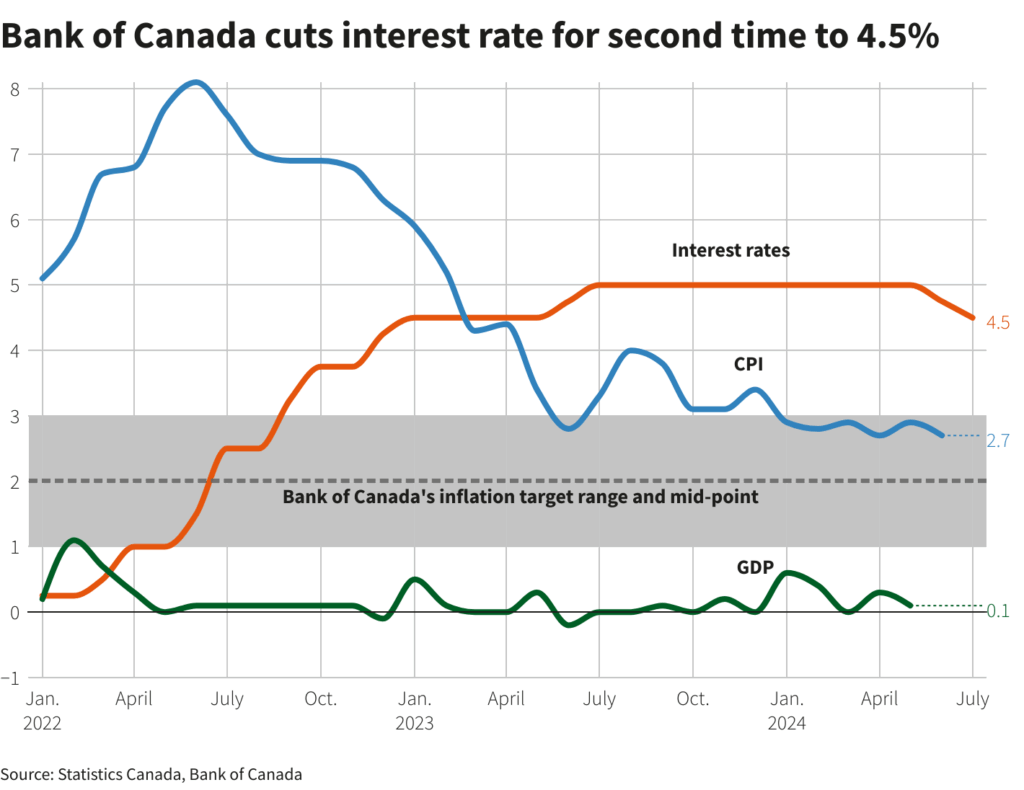
As of October 2023, the Bank of Canada has maintained its policy interest rate at 5.00%. The decision to hold rates steady comes in response to a combination of factors including inflation pressures, economic growth indicators, and global economic trends. This marks a significant period of higher interest rates, as just one year ago, the rate was notably lower at 1.00%.
The Bank of Canada’s strategy aims to combat persistent inflation, which rose to 6.8% in 2023, above the central bank’s target of 2%. Higher interest rates are typically employed to cool down an overheating economy and bring inflation under control.
Impact on Consumers and Businesses
The current interest rate environment has substantial effects on consumers. Mortgage rates have seen substantial increases, leading to higher monthly payments for homeowners. The average five-year fixed mortgage rate has climbed to approximately 7.0%. This increase puts additional financial pressure on Canadians, especially first-time homebuyers who are grappling with affordability challenges.
Similarly, higher interest rates affect personal loans and credit card debt. Consumers may find it more expensive to borrow, which can lead to a reduction in discretionary spending. Businesses, too, face increased costs for financing operations or expansion plans, potentially slowing economic growth.
Future Projections and Economic Implications
As we look toward the future, analysts remain divided on the direction of interest rates. While some predict potential cuts by the end of 2024 due to easing inflation, others warn that a resilient labor market may keep rates elevated longer than anticipated. Stakeholders, including homebuyers, investors, and policymakers, will need to monitor these developments closely.
In summary, the current landscape of bank interest rates in Canada is shaped by the ongoing battle against inflation and the need to foster a balanced economy. Understanding these rates and their implications is essential for consumers and businesses as they navigate financial decisions in an uncertain economic environment.



