Introduction
The Canada EV mandate represents a pivotal step in the nation’s journey towards a sustainable future. As concerns over climate change intensify, Canadian authorities recognize the importance of reducing greenhouse gas emissions from transportation, which is a significant contributor to the country’s carbon footprint. By committing to a comprehensive EV mandate, the government aims to promote electric vehicle adoption, enhance environmental sustainability, and support the transition to clean energy solutions.
Details of the Canada EV Mandate
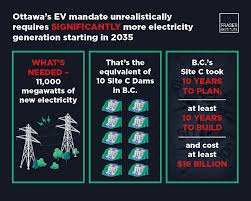
In August 2021, the Canadian government unveiled its ambitious roadmap for transitioning to electric vehicles as part of its broader commitment to achieving net-zero emissions by 2050. The mandate requires that by 2035, all light-duty vehicle sales in Canada will be zero-emission vehicles (ZEVs). This includes not only battery electric vehicles (BEVs) but also hydrogen fuel cell vehicles. The initiative aims to ensure that the automotive market is fully aligned with environmental goals, thus reducing dependency on fossil fuels.
To facilitate this transition, the government has outlined several key strategies, including significant investments in infrastructure for EV charging stations across the country, incentives for consumers to purchase ZEVs, and collaborative efforts with automotive manufacturers to boost production of electric vehicles. Major automakers have already announced plans to transition their fleets in line with the mandate, with several pledging to electrify their entire product lines.
Implications and Reactions
The implications of the Canada EV mandate are far-reaching. Environmental advocates have welcomed the initiative as a necessary measure for combating climate change and promoting sustainable practices. However, the mandate has also sparked concerns about the pace of change, with critics pointing out that substantial investment in infrastructure, workforce training, and supply chain adjustments are essential to make the transition feasible.
Additionally, the provinces will play a crucial role in implementing the mandate and developing local policies that complement federal initiatives. Some regions, like Quebec and British Columbia, are already leading in EV adoption, while others may face challenges in scaling up their infrastructure and consumer engagement.
Conclusion
The Canada EV mandate marks a significant turning point in the country’s efforts to reduce carbon emissions and foster a cleaner environment. As the world increasingly shifts towards electric mobility, the success of this mandate will rely on comprehensive planning and execution. With ongoing investments and public awareness initiatives, Canada can lead by example in the global movement towards sustainable transportation. For consumers, the transition presents not only challenges but also opportunities in embracing a future powered by clean energy.



