Introduction
The topic of interest rate cuts by the Bank of Canada has become increasingly significant as the country navigates economic challenges. These cuts aim to stimulate growth, control inflation, and provide relief to consumers and businesses. Understanding the implications of these rate adjustments is crucial for Canadians as they influence borrowing costs, investment decisions, and overall economic stability.
Recent Developments in Interest Rates
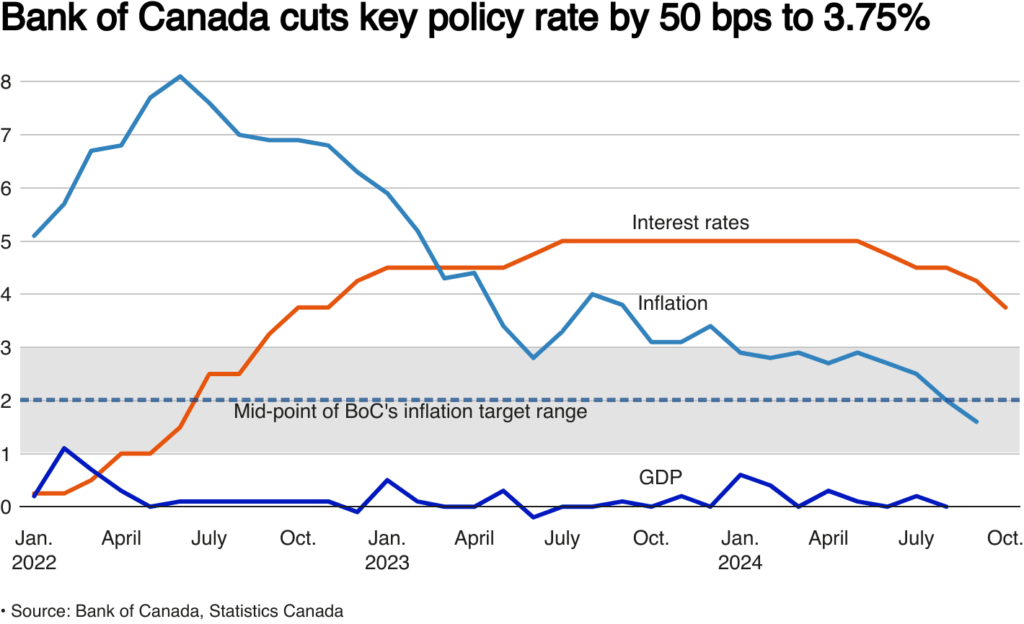
As of October 2023, the Bank of Canada has implemented a series of interest rate cuts to combat the negative effects of inflation and an uncertain economic environment. The most recent cut occurred during the bank’s monetary policy meeting in September 2023, where the benchmark interest rate was reduced from 5.00% to 4.75%. This marked the first interest rate cut since early 2022, signaling a shift in monetary policy aimed at stimulating spending and investment.
Impact on the Economy
The decision to lower interest rates is expected to have widespread repercussions. A reduction in rates generally lowers the cost of borrowing, making it more affordable for consumers to secure loans for homes, cars, and businesses. This increased access to credit can invigorate consumer spending, a critical component of Canada’s economic performance.
Furthermore, businesses may take advantage of lower financing costs to invest in expansion or hiring, potentially leading to job creation and a more robust economy. However, while these rate cuts provide immediate relief, there are concerns about the long-term ramifications of prolonged low-interest rates, including the risk of inflated asset prices and increased household debt.
Public Response and Forecasts
Reactions to the Bank of Canada’s interest rate cuts have been mixed. Homebuyers and businesses have praised the decreased borrowing costs; however, there are warnings from financial experts about managing debt levels responsibly. As Canadians respond to the changing economic landscape, it will be essential to monitor consumer behavior and overall economic indicators, such as inflation rates, unemployment, and GDP growth.
Conclusion
The recent interest rate cuts by the Bank of Canada are aimed at spurring economic activity in challenging times. While these cuts may lead to more favorable borrowing conditions for consumers and businesses alike, it is vital to consider the broader economic implications and potential risks associated with increased debt levels. As the situation evolves, Canadians must stay informed and prepare for changes in the economic landscape driven by these monetary policy adjustments.



