Introduction
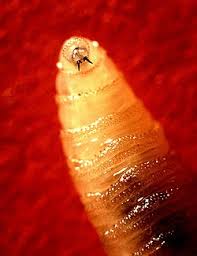
Screwworms, the larvae of the Cochliomyia hominivorax fly, are notorious pests that pose a significant threat to livestock health. Known for infesting wounds and causing severe damage, these parasites can lead to substantial economic losses in the agricultural sector. Recently, reports of screwworm infestations have prompted discussions on their relevance and the need for effective control measures, especially within Canada where agriculture is a vital part of the economy.
Current Events
As of late 2023, there has been an increasing vigilance amongst Canadian farmers and agricultural agencies regarding screwworms. In the last few months, sightings have been reported in regions close to the U.S.-Canada border, raising alarms due to the potential economic impact on livestock farming. Screwworm larvae typically invade the wounds of animals, feed on their flesh, and can lead to severe infections, loss of livestock, and increased veterinary costs. According to Statistics Canada, the livestock sector generated over $7 billion in revenues last year, making the risk of screwworm infestation a crucial concern for farmers and ranchers alike.
Control Measures
The Canadian government, in cooperation with agricultural organizations, has launched initiatives to educate livestock owners about prevention and treatment strategies for screwworm infestations. Programs include training on recognizing signs of infestation, proper wound management in animals, and implementing biosecurity measures to prevent the introduction of these pests into farms. In addition, research into biological control methods, such as sterile insect techniques (SIT), is ongoing. This method involves releasing sterilized male flies to reduce breeding populations safely.
Conclusions and Future Outlook
As the agricultural landscape continues to evolve, the threat posed by screwworms emphasizes the need for preparedness and proactive measures among livestock producers. With the rise in international travel and trade, the risk of spreading screwworms to previously unaffected areas remains. Experts recommend continuous monitoring, education, and collaboration across borders to mitigate the potential impacts on agriculture. Farmers must stay informed of the latest developments and prevention techniques to safeguard their livestock and mitigate potential losses. Through concerted effort and community engagement, it is hoped that screwworms can be kept at bay, ensuring the health of livestock and the sustainability of the agricultural industry in Canada.






