Introduction to Mpox
Mpox, formerly known as monkeypox, has emerged as a significant public health concern, particularly following the global outbreak in 2022 and 2023. This viral disease is caused by the monkeypox virus, closely related to the variola virus that causes smallpox. The importance of understanding mpox lies in its potential to spread and the implications it holds for public health systems worldwide. As health authorities continue to respond to this outbreak, awareness and education about the disease are vital for prevention and management.
Recent Developments
The World Health Organization (WHO) declared the mpox outbreak a public health emergency of international concern in July 2022, as cases surged in regions where the virus was not traditionally found. By October 2023, over 104,000 cases had been reported worldwide, with the majority occurring in North America and Europe. Governments and health organizations have since been actively working to contain the spread through vaccination campaigns and public education initiatives.
Vaccines, including modified ACAM2000 and JYNNEOS, have been deployed in high-risk populations to curb transmission. Health agencies stress the importance of vaccination, particularly for men who have sex with men, as they have been identified as the most affected demographic during the outbreak. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) has also shared guidelines for early detection, isolation, and treatment of mpox cases to minimize its impact.
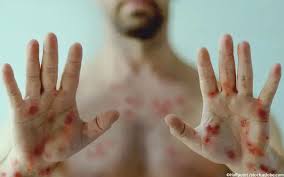
Symptoms and Transmission
Mpox presents symptoms similar to smallpox, including fever, lymphadenopathy, body aches, and a distinctive rash that may develop into lesions. Transmission primarily occurs through skin-to-skin contact with lesions, bodily fluids, or respiratory droplets from infected individuals. As such, understanding the routes of transmission is crucial for preventing outbreaks, particularly in communal settings and healthcare environments.
Conclusion: The Path Forward
The emergence of mpox highlights the need for continued vigilance and preparedness in the face of viral outbreaks. Public health experts predict that, without robust intervention and vaccination efforts, mpox could become endemic in new regions, posing long-term health risks. Ongoing global collaboration, research, and the dissemination of accurate information will be pivotal in managing mpox. For communities, staying informed and practicing preventive measures is essential to mitigate the spread and protect vulnerable populations.



