Introduction
Lyme disease is a tick-borne illness that has become increasingly relevant in Canada due to rising incidences reported in various regions. As warmer temperatures and shifting climatic patterns create favorable conditions for tick populations, understanding Lyme disease is crucial for public health and personal safety.
What is Lyme Disease?
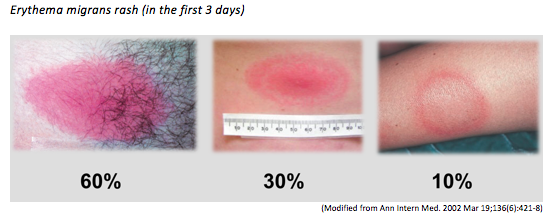
Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, which is primarily transmitted to humans through the bite of infected black-legged ticks, commonly known as deer ticks. Symptoms typically manifest as a characteristic circular rash known as erythema migrans, alongside flu-like symptoms that may include fever, headache, fatigue, and joint pain.
Increase in Cases
According to the Public Health Agency of Canada, reported cases of Lyme disease have significantly increased, particularly in provinces like Ontario, Quebec, and British Columbia. In 2021, there were over 3,000 reported cases, compared to about 1,000 in 2016. This upward trend is attributed to several factors, including changes in land use, increased public awareness, and rising tick populations due to climate change.
Public Health Response
Provincial health authorities are ramping up efforts to educate the public about Lyme disease prevention. Initiatives include distributing pamphlets that provide information on how to avoid tick bites, recognizing the signs and symptoms of the disease, and encouraging people to seek prompt medical attention if they suspect they have been bitten by an infected tick.
Preventative Measures
Prevention is key in managing Lyme disease risks. Experts recommend wearing long sleeves and pants when exploring wooded or grassy areas, using insect repellent containing DEET on exposed skin, and performing thorough tick checks after outdoor activities. Additionally, homeowners are encouraged to maintain their properties by clearing tall grasses and brush where ticks are likely to reside.
Conclusion
As Lyme disease continues to spread in Canada, raising awareness and understanding its prevention is vital for reducing risks associated with this illness. With increasing variations in climate, the public must stay informed and vigilant. Regular check-ups, education, and outreach programs will be essential components in combating the potential threats of Lyme disease in the coming years.



