Introduction
Nuclear weapons remain one of the most significant and contentious issues in global politics today. With the potential for massive destruction and threats to international peace, understanding which countries possess these weapons is critical. While the 1968 Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty (NPT) aimed to limit the spread of nuclear weapons, as of 2023, nine countries are known to maintain nuclear arsenals. This article seeks to provide an overview of these nations and the implications of their nuclear capabilities.
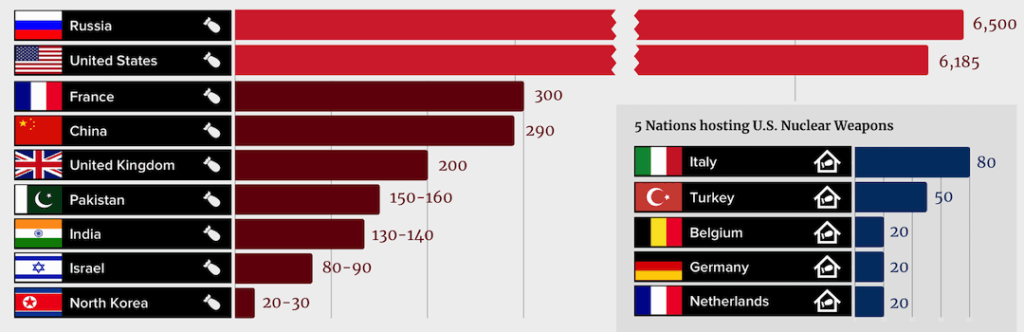
List of Countries with Nuclear Weapons
1. **United States**: The first country to develop nuclear weapons, the U.S. has an estimated 5,800 nuclear warheads. The U.S. maintains a policy of nuclear deterrence and has been involved in various arms control agreements, such as the New START treaty with Russia.
2. **Russia**: With approximately 6,375 nuclear warheads, Russia holds the largest stockpile. The geopolitical tension between the U.S. and Russia continues to influence global nuclear policy.
3. **China**: China is steadily increasing its nuclear capabilities, currently estimated at about 3,000 warheads. The expansion of China’s nuclear arsenal has raised concerns, especially in the Asia-Pacific region.
4. **France**: France has around 290 nuclear warheads and maintains a policy of nuclear independence. They focus on strategic deterrence, particularly concerning threats from regional rivals.
5. **United Kingdom**: With a stockpile of approximately 225 nuclear weapons, the UK is committed to reducing its arsenals under international treaties.
6. **Pakistan**: Pakistan’s estimated 170 nuclear warheads are largely a response to rival India’s nuclear capabilities. The region remains a focal point of nuclear tension.
7. **India**: With an estimated 160 nuclear warheads, India developed its program independently and perceives its nuclear capability as essential for national security.
8. **North Korea**: North Korea’s nuclear ambitions have triggered major international concerns. Current estimates suggest around 40-50 nuclear warheads, and ongoing tests have led to strict sanctions from the international community.
9. **Israel**: While Israel maintains a policy of ambiguity regarding its nuclear arsenal, it is widely believed to possess approximately 90 nuclear warheads. Israel views its nuclear capability as crucial to its national security given the hostile environments it faces.
Conclusion
The existence of nuclear weapons in these nine countries not only poses a direct threat but also plays a significant role in global security dynamics. Continued dialogue and negotiation efforts, such as arms control treaties and disarmament talks, are critical in preventing nuclear conflicts. As tensions in various regions escalate, the implications of nuclear proliferation remain pressing, making the understanding of this issue more vital than ever for policymakers and global citizens alike. The ongoing challenge will be to ensure that nuclear weapons do not fall into the wrong hands while pursuing pathways to global disarmament.



