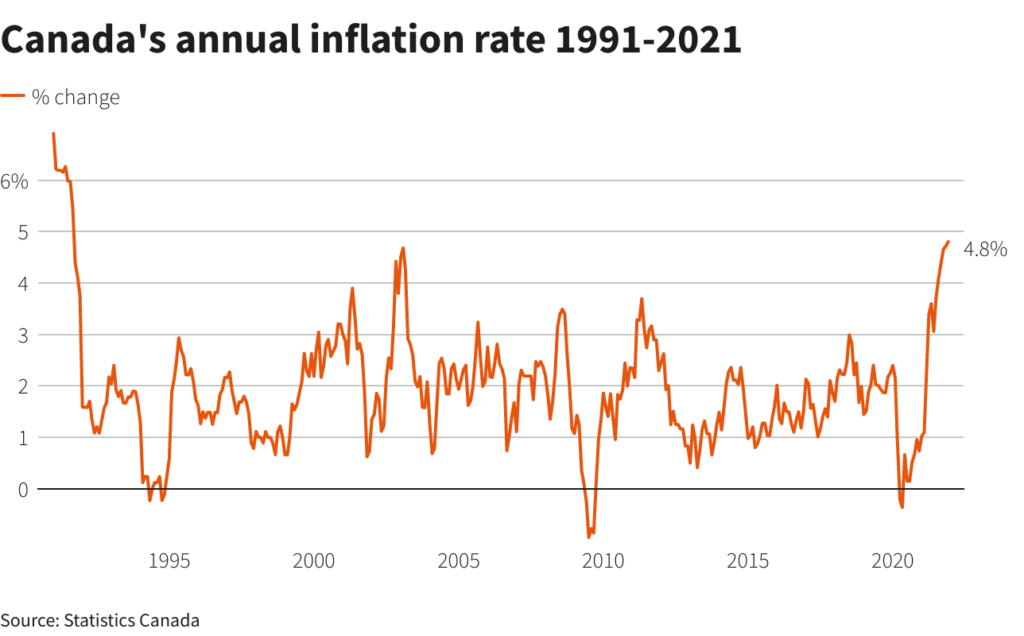
Introduction
As Canada navigates through post-pandemic recovery, inflation has emerged as a pressing issue affecting all Canadians. Inflation, defined as the rate at which general prices for goods and services rise, is a crucial indicator of economic health and can have far-reaching consequences on purchasing power and financial stability. With inflation reaching levels not seen in decades, understanding its causes and effects is more relevant than ever for households and policymakers alike.
Current Inflation Trends in Canada
As of October 2023, Canada’s inflation rate was reported at approximately 6.9%, a significant increase compared to previous years. Year-on-year, this marks a dramatic rise, driven by various factors including supply chain disruptions, increased demand for goods, and escalating energy prices. Food inflation has particularly hit low-income households hard, with prices for essential items like bread, meat, and dairy soaring by as much as 10-15%.
The Bank of Canada has responded to rising inflation by adjusting interest rates to slow down economic growth and stabilize prices. In contrast, the Canadian dollar has faced fluctuation, causing international imports to grow more expensive, further exacerbating the inflationary trends.
The Impacts of Inflation on Canadians
The direct impact of inflation is seen in the strain on household budgets. Families are forced to re-evaluate their spending patterns, with everyday necessities taking up a more significant portion of their income. Many Canadians are reporting a decrease in savings and an increased reliance on credit cards to maintain their living standards.
Businesses are also feeling the pressure, struggling with rising operational costs while attempting to maintain competitive pricing. The ensuing cycle of increased costs and higher prices can lead to eroded consumer confidence and dampened economic growth.
Looking Ahead: What’s Next?
As inflation continues to dominate economic discussions, forecasts suggest that it may begin to ease by mid-2024 thanks to proactive measures by the Bank of Canada and recovery signs in global supply chains. However, analysts caution that uncertainty remains, particularly with potential geopolitical tensions and fluctuating oil prices.
In conclusion, understanding Canada’s inflation landscape is crucial for both individuals and businesses alike. Stakeholders must remain vigilant, adjusting strategies as economic indicators evolve. Canadians will need to adapt to new financial realities while advocating for policies that address the root causes of inflation, ensuring economic stability for future generations.



