Introduction
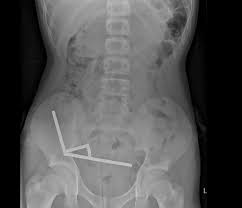
Swallowing magnets has become an alarming issue, particularly among young children who may mistake small magnets for candy. The ingestion of magnets can lead to severe health complications, including intestinal blockages and perforations, making it crucial for parents and guardians to understand the risks involved. In recent years, reports of children being hospitalized after swallowing magnets have increased, catalyzing important discussions surrounding toy safety regulations and parental vigilance.
Health Risks Associated with Ingesting Magnets
The dangers of ingesting magnets are well-documented among health professionals. When a child swallows more than one magnet, the strong forces can attract each other through the walls of the intestines, leading to serious complications. According to a report from the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission, between 2000 and 2020, at least 2,700 incidents involving children swallowing magnets were reported. These incidents often resulted in emergency surgeries, highlighting the potential for life-threatening injuries.
Recent Incidents and Ongoing Concerns
In Canada, health authorities have expressed concern over the increasing prevalence of magnet ingestion cases, particularly with the rise of high-powered neodymium magnets available online. In 2022, hospitals across the country reported a surge in cases of children, aged 5 and under, requiring medical attention due to magnet ingestion. Medical experts recommend that parents secure magnets and magnet-containing toys well out of children’s reach to mitigate risks.
Moreover, Canadian safety regulations around magnetic toys have been scrutinized, and public health advocates are calling for stricter regulations and mandatory warning labels on products that contain small magnets. The potential for mischief and accidental ingestion poses a major risk, especially in households with multiple children.
Prevention and Awareness Strategies
Raising awareness about the dangers associated with swallowing magnets is key to preventing future incidents. Educational initiatives targeting parents, caregivers, and manufacturers can significantly reduce the number of accidents. Parents are encouraged to supervise children during playtime and to choose toys that comply with current safety standards.
Conclusion
The risks associated with swallowing magnets are stark, and the responsibility to prevent such occurrences lies not only with parents but also manufacturers and regulatory bodies. As more cases surface, the importance of public awareness and stringent safety measures cannot be understated. By staying informed and vigilant, caregivers can protect children from the potentially life-threatening consequences of swallowing magnets.



