Introduction
The state of interest rates set by the Bank of Canada is critical for Canadian consumers and businesses. As the nation’s central bank, its monetary policy decisions influence borrowing costs, economic growth, and inflation. Understanding these rates and their fluctuations is essential for making informed financial decisions.
Recent Developments
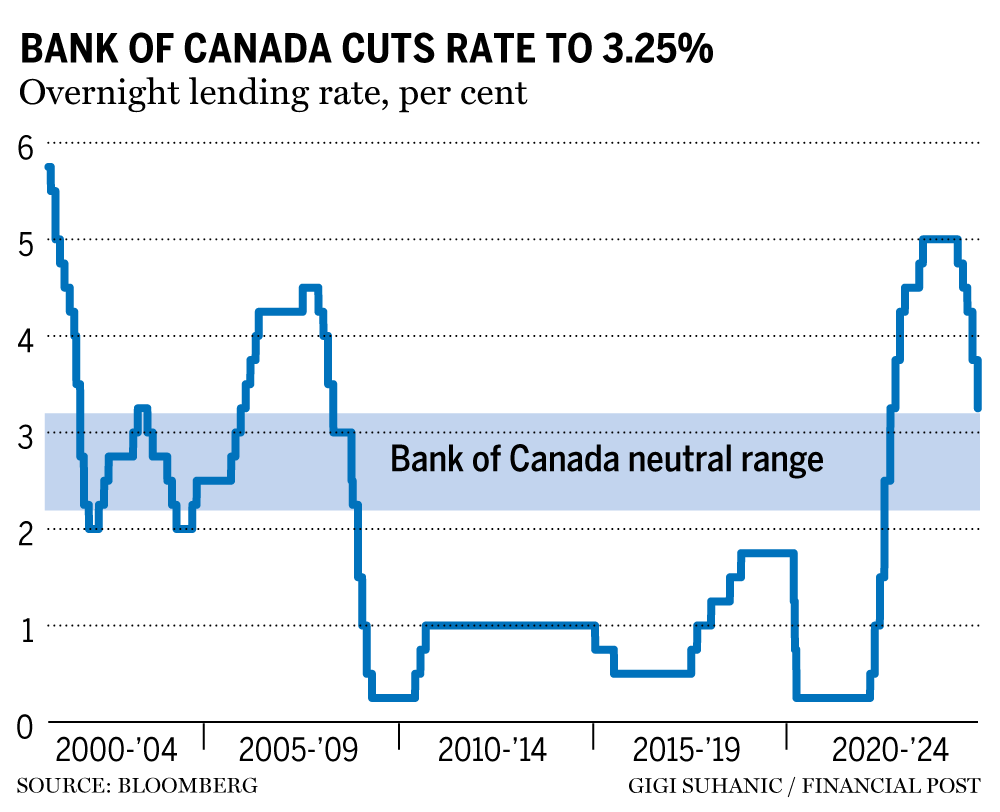
As of October 2023, the Bank of Canada has maintained its overnight interest rate at 5.00%, unchanged since July. This level is among the highest seen since 2001 when rates peaked at over 6.0%. Bank officials have cited the need to manage persistent inflation, which has seen consumer prices rise by about 4.0% year over year. While this is a decrease from the 8.1% peak in mid-2022, it remains above the Bank’s target of 2.0%.
In the September rate announcement, Governor Tiff Macklem stated that conditions are still tight in the economy, indicating that higher rates are essential in slowing down excessive spending and bringing inflation closer to target. However, some economists believe that holding rates steady may also signal the Bank’s preparedness to consider future rate cuts if economic growth continues to falter.
Impact on the Economy
The high interest rates have significant implications for Canadian households and businesses. Many variable-rate mortgage holders have felt the strain as their monthly payments have risen, leading to calls for more government support for vulnerable families. Additionally, small businesses reliant on loans for operational costs face higher financing costs, which can hinder economic growth.
Analysts anticipate that the Bank of Canada may hold the line on interest rates for the remainder of the year as it assesses economic data. The tight labour market and sustained consumer demand could prolong the period of high rates unless inflation moves towards acceptable levels. Future communication from the Bank will be crucial for understanding the direction of economic policy.
Conclusion
The interest rate set by the Bank of Canada plays a vital role in shaping the financial landscape of the country. For individuals and businesses, remaining informed on these updates is crucial for navigating loans, mortgages, and broader economic conditions. Observers speculate that if inflation continues to decline and economic indicators soften, the Bank may be compelled to lower rates in early 2024. Monitoring these developments will be essential for all Canadians as they make financial and investment decisions in the coming months.



