Introduction
As climate events continue to shape global weather patterns, Hurricane Erin has emerged as a significant meteorological event that reached the shores of Scotland. Understanding the implications of this weather phenomenon is essential for local residents, government agencies, and climatologists alike due to its potential for disruption, resulting impacts on infrastructure, natural ecosystems, and public safety.
Details of Hurricane Erin
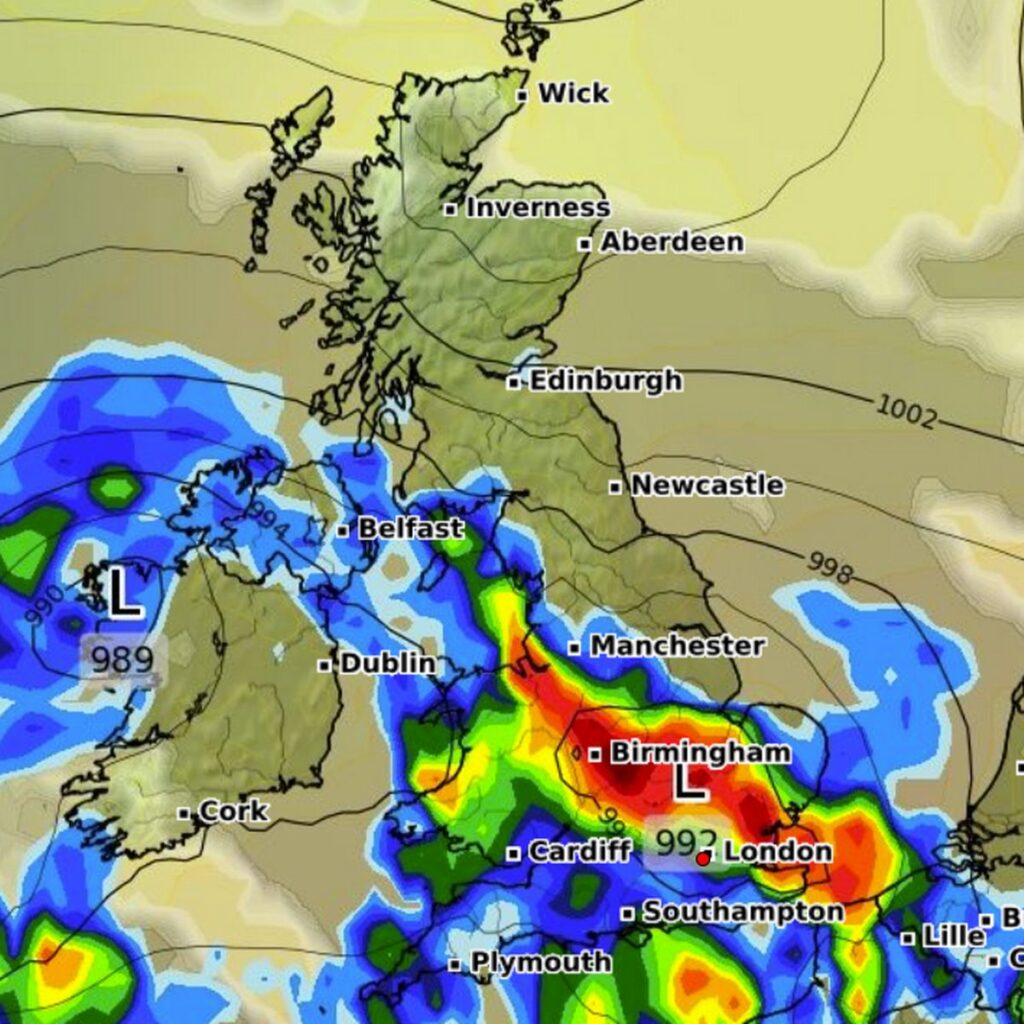
Hurricane Erin formed in the Atlantic Ocean in early September 2023, characterized by intense rain, high winds, and rising sea levels. Classified as a category 2 hurricane, it tracked toward the northeastern coast of the United States before receding across the Atlantic. By mid-September, the remnants of Erin had made their way to Scotland, bringing with it heavy rainfall and strong winds that impacted numerous regions, especially coastal areas in western and northern Scotland.
The Scottish Environment Protection Agency (SEPA) issued several flood warnings as water levels began to rise. In towns such as Oban and Fort William, residents reported significant flooding that disrupted daily life, including cancelled ferry services, closed schools, and power outages affecting thousands. Emergency services mobilized to address the immediate risks, with authorities urging residents in vulnerable areas to remain vigilant and prepared for further adverse conditions.
Government Response and Community Impact
The Scottish government activated an emergency response strategy, securing necessary resources to assist affected communities. Relief efforts included the deployment of personnel from police, fire, and medical services, who worked tirelessly to ensure public safety and provide support to those impacted. Community centers opened their doors to offer shelter to families forced to evacuate their homes.
Long-term implications of Hurricane Erin may also lead to renewed discussions regarding climate change and infrastructure resilience in Scotland. As extreme weather events become more frequent, local governments may need to consider investing in enhanced drainage systems and coastal defenses to safeguard against future storms.
Conclusion
The arrival of Hurricane Erin in Scotland serves as a stark reminder of the increasing volatility of weather patterns due to climate change. It highlights the need for preparedness among residents and adaptability in policy-making. As communities recover, the focus will shift to rebuilding and strengthening their infrastructures against subsequent weather events, prompting discussions on sustainability and climate resilience. Future forecasts after Erin indicate the possible continuation of unpredictable weather patterns in the region, underlining the importance of ongoing monitoring and community engagement in climate adaptation strategies.



