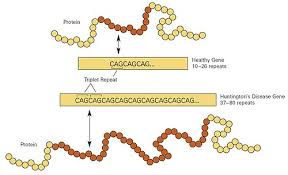
Introduction to Huntington Disease
Huntington disease (HD) is a progressive genetic disorder characterized by the degeneration of nerve cells in the brain. It significantly impacts an individual’s cognitive abilities, movement, and overall quality of life. This disorder is caused by a mutation in the HTT gene and is often inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern. Understanding Huntington disease is crucial as its onset usually occurs in mid-adulthood, affecting not only patients but their families as well.
Understanding the Symptoms and Stages
Symptoms of Huntington disease typically emerge between the ages of 30 and 50, but juvenile forms can also occur. Early manifestations include mood swings, irritability, and changes in cognitive function. As the disease progresses, patients may experience severe motor dysfunction, including uncontrolled movements known as chorea, along with significant cognitive decline that may lead to dementia.
Huntington disease progresses through several stages. The early stage is often marked by subtle changes in personality and coordination. As the condition advances to middle and late stages, individuals may face severe difficulties with daily activities, resulting in a loss of independence.
Latest Research and Advances
Recently, researchers have made significant strides in understanding Huntington disease, focusing on gene therapy and potential treatments that may slow its progression. In 2023, clinical trials have tested antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) designed to reduce the production of the toxic huntingtin protein responsible for neuronal death. Initial results show promise in both safety and efficacy, highlighting the potential for breakthrough therapies.
Conclusion: The Future of Huntington Disease Management
Despite the challenges posed by Huntington disease, ongoing research offers hope for patients and families affected by this devastating disorder. As understanding of the disease increases, so does the potential for developing effective therapies. Advocacy efforts are essential, emphasizing the need for funding and resources to combat Huntington disease. With advancements in genetic research and potential treatments on the horizon, there is optimism for improved management and quality of life for individuals diagnosed with Huntington disease in the future.



