Introduction
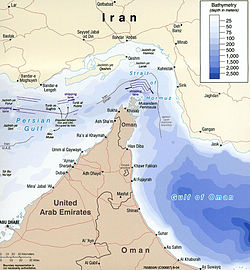
The Strait of Hormuz, located between Oman and Iran, is one of the world’s most crucial maritime chokepoints. Approximately 20% of the world’s oil supply passes through this narrow waterway, making its map not just a geographical asset but a vital tool in global energy security. Understanding the Strait of Hormuz is essential, given its influence on international trade, politics, and security dynamics.
Geographical Overview
Measuring approximately 39 kilometers in width at its narrowest point, the Strait connects the Persian Gulf to the Gulf of Oman. The map of the Strait of Hormuz highlights not only its strategic location but also surrounding countries including Iran, Oman, and the United Arab Emirates. Various maritime routes emerge from it, directing oil tankers towards global markets, primarily in Asia, Europe, and North America.
Geopolitical Significance
The Strait of Hormuz has been a focal point in international relations, especially regarding U.S.-Iranian tensions. In recent months, military maneuvers and political rhetoric have intensified, leading to increased surveillance and naval presence from various countries, including the United States and its allies. Maps detailing naval routes and territorial waters are crucial for monitoring shipping lanes, assessing risks, and ensuring the safety of maritime traffic.
According to the U.S. Energy Information Administration, geopolitical instability in the region could impact oil prices significantly. Disruptions in the Strait due to political conflicts or military encounters could have a ripple effect globally, emphasizing the importance of monitoring this area through accurate mapping.
Economic Implications
The Strait of Hormuz is not just important from a strategic standpoint but also from an economic perspective. A report by the International Energy Agency highlighted that about 80% of the oil exported from the Gulf region passes through this strait. Any disruption can lead to immediate spikes in oil prices, affecting consumers and economies around the world.
Conclusion
The map of the Strait of Hormuz serves as a clear representation of a vital passage in global trade and politics. As tensions in the region fluctuate, understanding this geographical zone’s implications on global energy supplies becomes increasingly critical. For governments, corporations, and consumers alike, staying informed about developments concerning the Strait of Hormuz will be vital in anticipating changes in energy supply and prices in the coming years. As we look ahead, the strategic importance of this choke point will likely continue to shape international relations and energy policies across the globe.



