Introduction
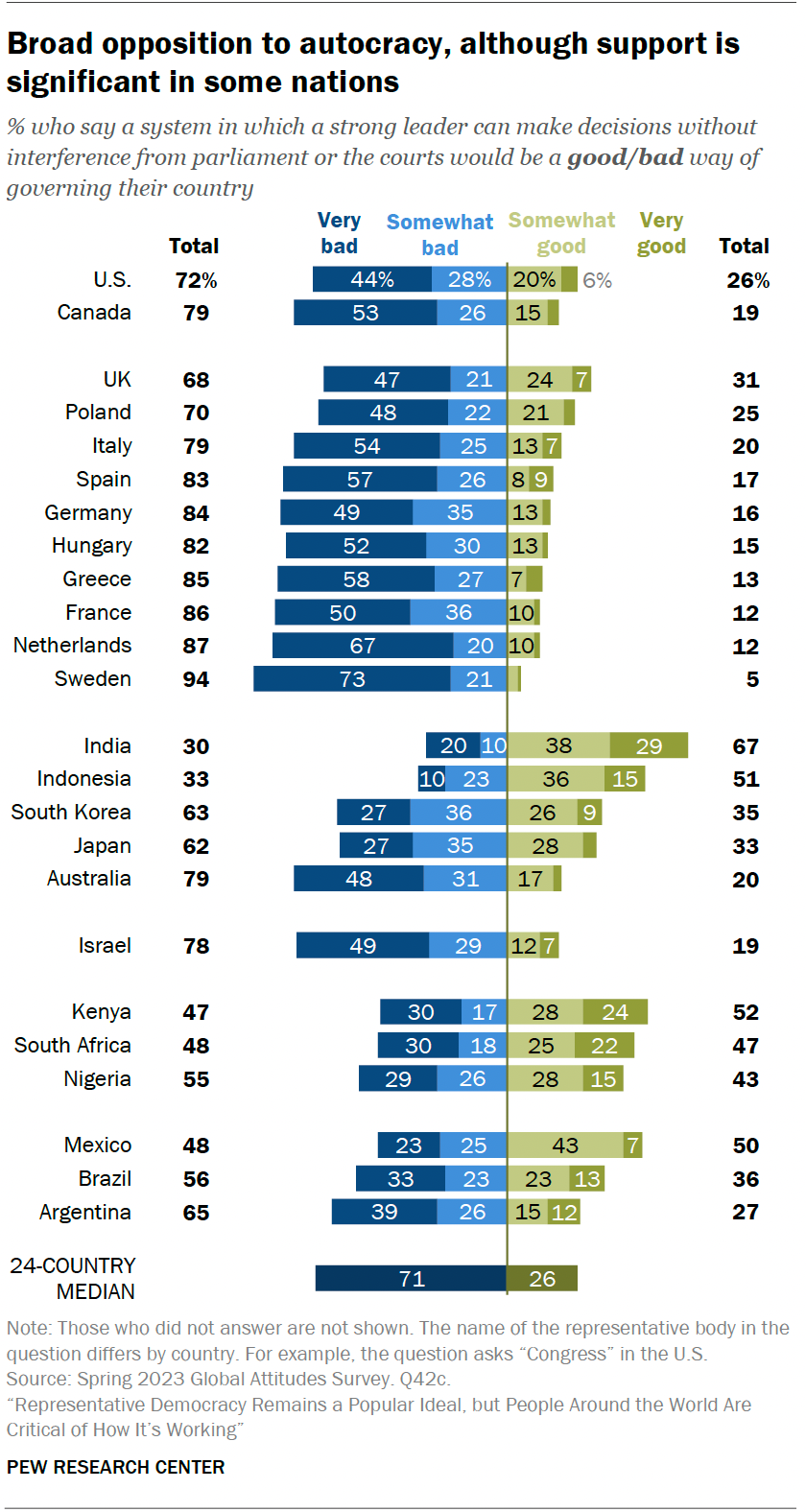
Autocracy, a form of government in which a single person or a small group wield unchecked power, is increasingly relevant in today’s global political landscape. The significance of understanding autocracy lies not only in its impact on nations but also in its influence on democracy, human rights, and international relations. As we witness a resurgence of autocratic leaders around the world, recognizing the characteristics and consequences of this governance style becomes vital for citizens and policymakers alike.
Recent Developments
In the past year, several countries have seen a rise in authoritarian practices. According to a report by Freedom House, the global trend towards autocracy is alarming, with numerous nations experiencing significant declines in political freedoms and civil liberties. For instance, countries such as Belarus and Myanmar have been cited as examples where autocratic regimes have suppressed dissent and curbed free speech following disputed elections.
The situation in Russia has also garnered international attention, particularly after the invasion of Ukraine. Kremlin’s tight grip on power under President Vladimir Putin exemplifies the shift towards autocracy, as independent media outlets have been silenced, and political opposition has faced severe repercussions.
Global Implications
The rise of autocracy does not only threaten the nations directly involved; it poses challenges to global democracy. As autocratic states strengthen their ties, they often exchange strategies and resources to undermine democratic institutions worldwide. For example, the close relationship between China and Russia has led to shared tactics in censorship and surveillance, impacting not just their internal affairs but also influencing neighboring regions.
Moreover, various global organizations are responding to the challenges of autocracy. The United Nations and regional entities are increasingly focused on promoting democracy and human rights, yet these initiatives often face backlash in autocratic regimes, resulting in strained diplomatic relations and heightened tensions.
Conclusions
Understanding autocracy’s implications is crucial for fostering democratic resilience. With ongoing trends indicating a potential for further autocratic governance globally, it is essential for citizens to remain informed and engaged. Universities, think tanks, and civil society organizations are instrumental in advocating for democratic values and accountability, shining a light on the actions of those in power.
As international dynamics continue to evolve, the fight against autocracy should remain a priority. The development and support of democratic institutions and practices must be upheld to ensure a more equitable and just world. The future of democracy depends on the collective efforts of individuals and nations to stand against the tide of autocratic governance.



